spring-boot virtual threads vs webflux
Abstract
Spring webflux is 57% faster than spring-boot that uses virtual threads on the benchmark to verify a JWT token in a MYSQL database. It doesn’t look like we’re getting any benefit of using virtual threads…
Following a prolific run of articles assessing the performance of a range of technologies, including Node.js, Deno, Bun, Rust, Go, Spring, Python, and more in the context of a simple “hello world” scenario, I received consistent feedback. While these articles garnered praise, there was a common refrain: they didn’t directly address real-world use cases. Readers urged me to extend the analysis to encompass more practical scenarios. Remarkably, these articles continued to draw a substantial number of views. Nevertheless, the point was well-founded. As a starting point, “hello world” is ideal, but it falls significantly short of representing real-world complexities.
Real-world use case
This article is a segment of our ongoing series aimed at dissecting various technologies through the lens of real-world scenarios. In this particular case, we’re delving into the following common use case:
- Extract a JWT from the authorization header.
- Validate the JWT and extract the user’s email from its claims.
- Execute a MySQL query using the extracted email.
- Finally, return the user’s record.
While this scenario may seem straightforward, it encapsulates a frequently encountered real-world challenge in the realm of web development.
Technologies
In this article, we’ll dive into a friendly comparison between siblings, SpringBoot with virtual threads and Webflux, focusing on their performance in a specific use-case scenario. We’ve already explored how a standard SpringBoot application stacks up against webflux, but now, we introduce a crucial differentiator:
Spring Boot with Virtual Threads
We have SpringBoot, but with a twist — it’s running on virtual threads instead of traditional physical threads. Virtual threads are a game-changer in the realm of concurrency. These lightweight threads simplify the often complex task of developing, maintaining, and debugging high-throughput concurrent applications. While virtual threads still operate on underlying OS threads, they introduce a remarkable efficiency improvement. When a virtual thread encounters a blocking I/O operation, the Java runtime temporarily suspends it, freeing up the associated OS thread to serve other virtual threads. This elegant solution optimizes resource allocation and enhances overall application responsiveness.
SpringBoot Webflux
On the other side of the ring, we have Spring Boot Webflux. Spring Boot WebFlux is a reactive programming framework within the Spring ecosystem, designed to build highly scalable and asynchronous web applications. It leverages the Project Reactor library to enable non-blocking, event-driven programming. Spring Boot WebFlux is particularly well-suited for applications that require high concurrency and low latency, making it an excellent choice for building reactive microservices and real-time, data-intensive applications. With its reactive approach, it allows developers to efficiently handle a large number of concurrent requests while still providing the flexibility to integrate with various data sources and communication protocols.
With these intriguing setups in mind, let’s delve deeper into our performance comparison.
Testing Environment and Software Versions
Our performance tests were conducted on a MacBook Pro M1 equipped with 16GB of RAM, ensuring a reliable testing platform. The software stack utilized for these tests includes:
- SpringBoot 3.1.3 (Running on Java 20)
- Preview mode enabled to get the power of virtual threads
SpringBoot and Supporting Libraries
Our setup involved the use of the following key components:
- SpringBoot 3.1.3 with Java 20 (preview mode to get VT)
- jjwt for JWT verification and decoding, enhancing the security of our application.
- mysql-connector-java for performing MySQL queries, maintaining data integrity and consistency.
Load Testing and JWTs
To evaluate the performance of our applications under varying loads, we employed the open-source load testing tool, Bombardier. Our test scenario involved a pre-created list of 100,000 JWTs. During testing, Bombardier randomly selected JWTs from this pool and included them in the Authorization header of the HTTP requests.
MySQL Database Schema
The MySQL database used for these performance tests featured a table named users. This table was designed with 6 columns, good enough to simulate real-world data interactions within our applications, enabling us to assess their responsiveness and scalability.
mysql> desc users;
+--------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| email | varchar(255) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| first | varchar(255) | YES | | NULL | |
| last | varchar(255) | YES | | NULL | |
| city | varchar(255) | YES | | NULL | |
| county | varchar(255) | YES | | NULL | |
| age | int | YES | | NULL | |
+--------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)The user database has been primed with an initial dataset containing a substantial 100,000 user records.
mysql> select count(*) from users;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 99999 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)In the context of our friendly performance evaluation between SpringBoot virtual threads and Webflux, it’s essential to understand a crucial data relationship. Specifically, within the JSON Web Token (JWT) payload, each email entry corresponds directly to a user record stored in our MySQL database.
Code
SpringBoot (virtual threads)
server.port=3000
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=testuser
spring.datasource.password=testpwd
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverpackage com.example.demo;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Table;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
public class User {
@Id
private String email;
private String first;
private String last;
private String city;
private String county;
private int age;
public String getId() {
return email;
}
public void setId(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getFirst() {
return first;
}
public void setFirst(String name) {
this.first = name;
}
public String getLast() {
return last;
}
public void setLast(String name) {
this.last = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getCounty() {
return county;
}
public void setCounty(String county) {
this.county = county;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@SpringBootApplication
public class UserApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public TomcatProtocolHandlerCustomizer<?> protocolHandlerVirtualThreadExecutorCustomizer() {
return protocolHandler -> {
protocolHandler.setExecutor(Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor());
};
}
}package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.util.Optional;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jws;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
import io.jsonwebtoken.security.Keys;
import java.security.Key;
import com.example.demo.UserRepository;
import com.example.demo.User;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
private SignatureAlgorithm sa = SignatureAlgorithm.HS256;
private String jwtSecret = System.getenv("JWT_SECRET");
@GetMapping("/")
public User handleRequest(@RequestHeader(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION) String authHdr) {
String jwtString = authHdr.replace("Bearer","");
Claims claims = Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey(jwtSecret.getBytes())
.parseClaimsJws(jwtString).getBody();
Optional<User> user = userRepository.findById((String)claims.get("email"));
return user.get();
}
}package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import com.example.demo.User;
public interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<User, String> {
}SpringBoot Webflux
server.port=3000
spring.r2dbc.url=r2dbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb
spring.r2dbc.username=dbser
spring.r2dbc.password=dbpwdpackage webfluxdemo;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
public class User {
@Id
private String email;
private String first;
private String last;
private String city;
private String county;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String email, String first, String last, String city, String county, int age) {
this.email = email;
this.first = first;
this.last = last;
this.city = city;
this.county = county;
this.age = age;
}
public String getId() {
return email;
}
public void setId(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getFirst() {
return first;
}
public void setFirst(String name) {
this.first = name;
}
public String getLast() {
return last;
}
public void setLast(String name) {
this.last = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getCounty() {
return county;
}
public void setCounty(String county) {
this.county = county;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}package webfluxdemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.r2dbc.connection.init.ConnectionFactoryInitializer;
import org.springframework.r2dbc.connection.init.ResourceDatabasePopulator;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.config.EnableWebFlux;
import io.r2dbc.spi.ConnectionFactory;
@EnableWebFlux
@SpringBootApplication
public class UserApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserApplication.class, args);
}
}package webfluxdemo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import webfluxdemo.User;
import webfluxdemo.UserService;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jws;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Claims;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
import io.jsonwebtoken.security.Keys;
import java.security.Key;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
private SignatureAlgorithm sa = SignatureAlgorithm.HS256;
private String jwtSecret = System.getenv("JWT_SECRET");
@GetMapping("/")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
public Mono<User> getUserById(@RequestHeader(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION) String authHdr) {
String jwtString = authHdr.replace("Bearer","");
Claims claims = Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey(jwtSecret.getBytes())
.parseClaimsJws(jwtString).getBody();
return userService.findById((String)claims.get("email"));
}
}package webfluxdemo;
import org.springframework.data.r2dbc.repository.R2dbcRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import webfluxdemo.User;
public interface UserRepository extends R2dbcRepository<User, String> {
}package webfluxdemo;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import webfluxdemo.User;
import webfluxdemo.UserRepository;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
public Mono<User> findById(String id) {
return userRepository.findById(id);
}
}Results
In our quest to assess the performance, we conducted a rigorous series of tests. Each test consisted of a staggering 5 million requests, and we assessed their performance under varying levels of concurrent connections: 50, 100, and 300.
Now, let’s dive into the results, presented in a compact tabular format:
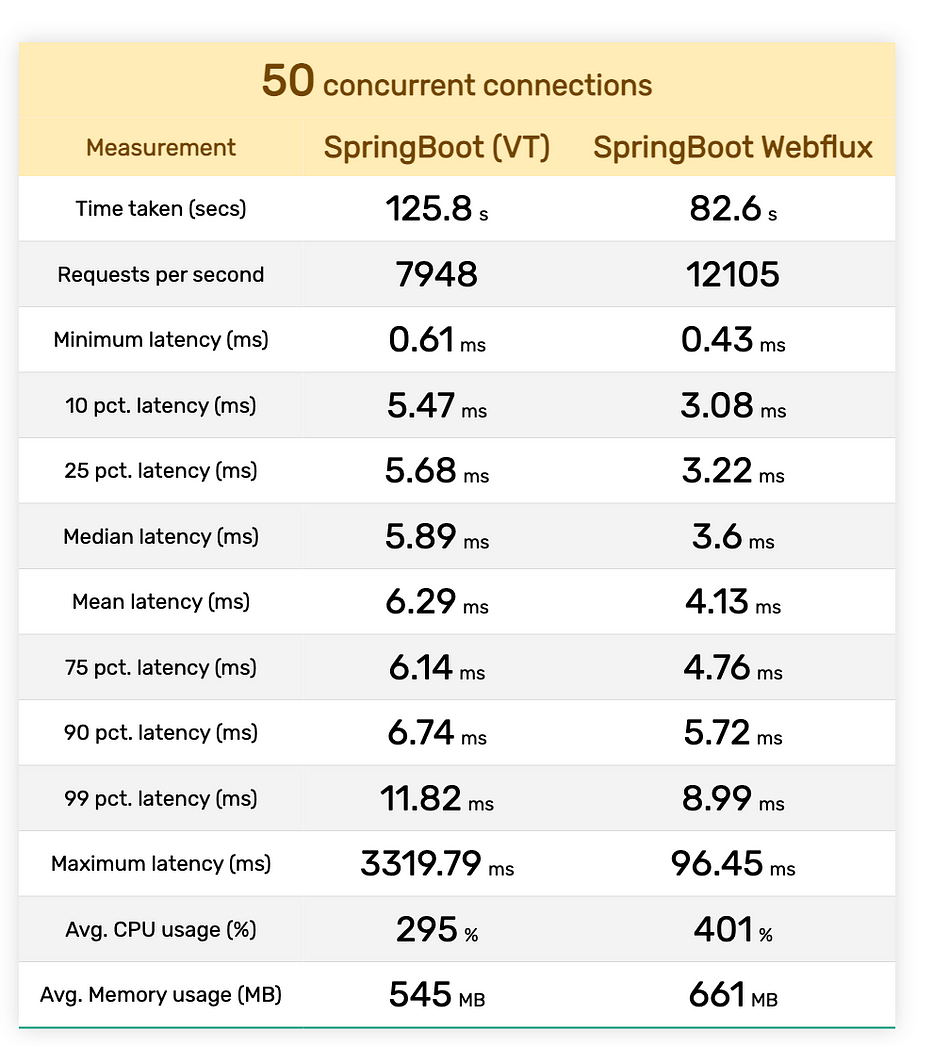
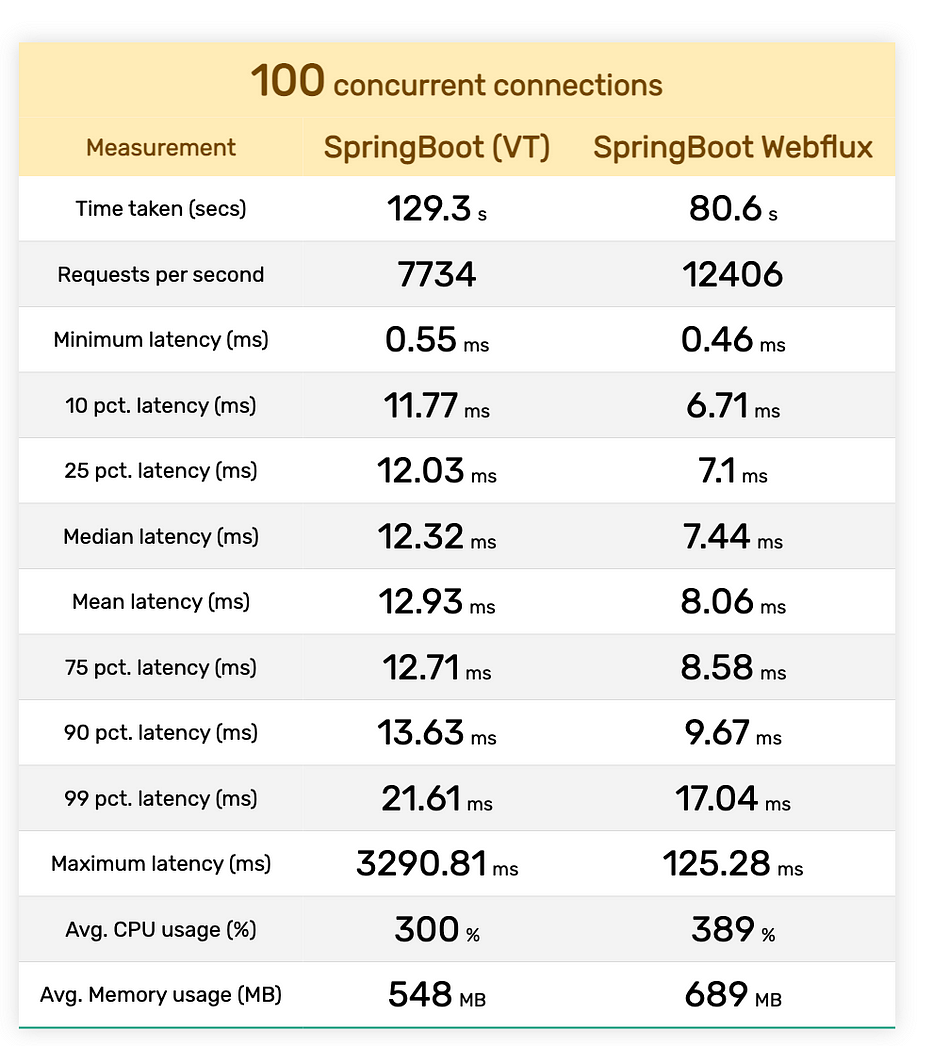
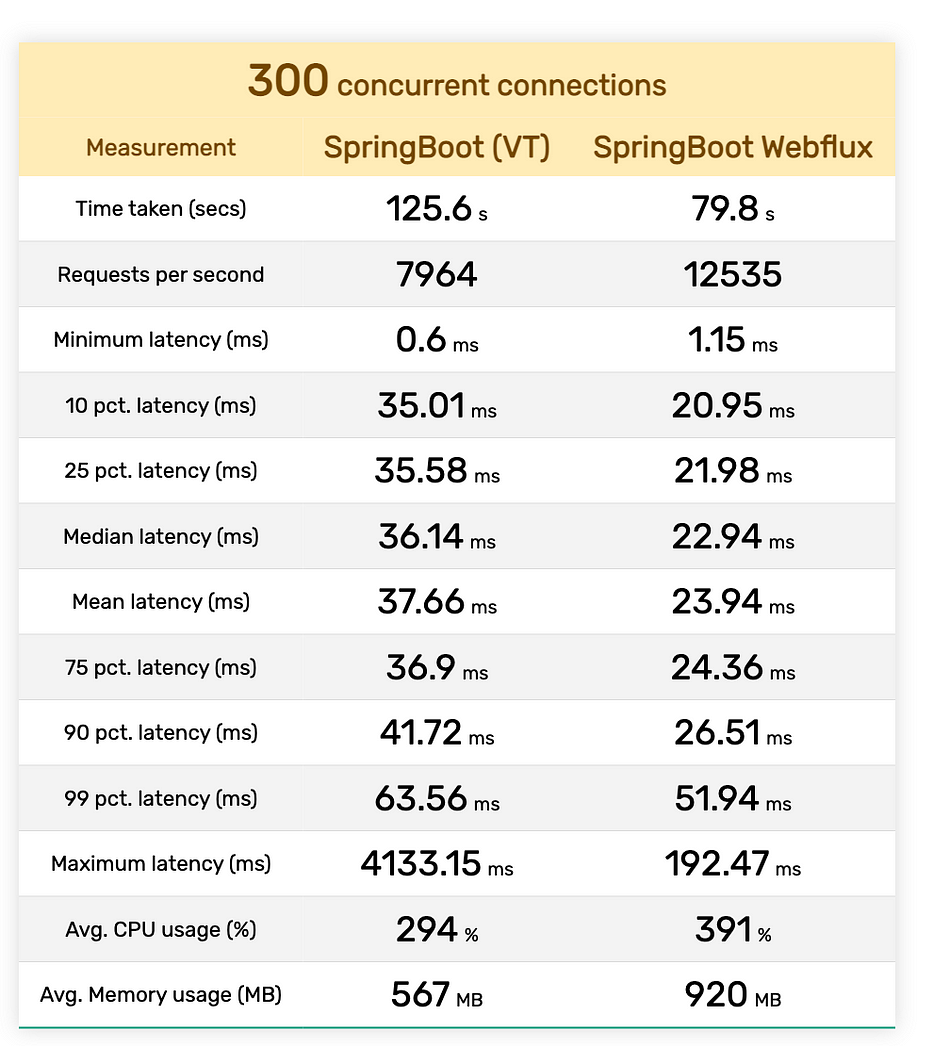
Conclusion
A scorecard is generated from the results using the following formula. For each measurement, get the winning margin. If the winning margin is:
- < 5%, no points are given
- between 5% and 20%, 1 point is given to the winner
- between 20% and 50%, 2 points are given to the winner
-
50%, 3 points are given to the winner
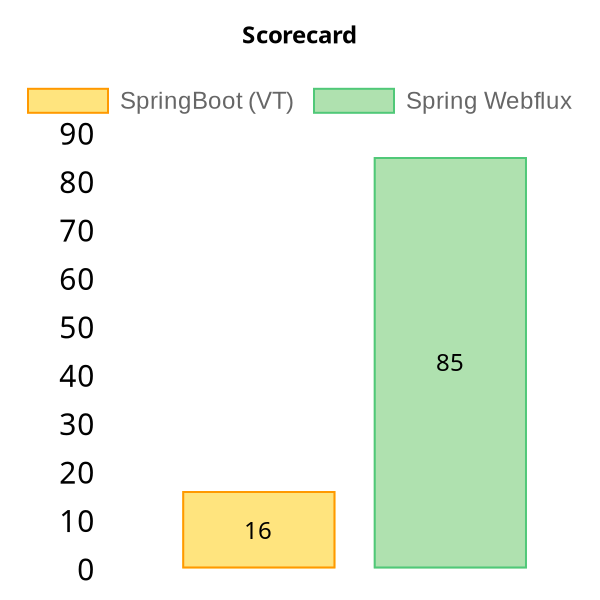
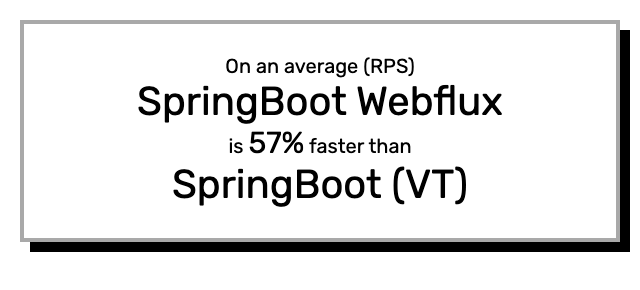
It doesn’t look like that we’re getting any benefits of using virtual threads over webflux even for real-world cases like this one. If you like to share, please add your expert opinion about virtual threads in the comments.