Api gateway
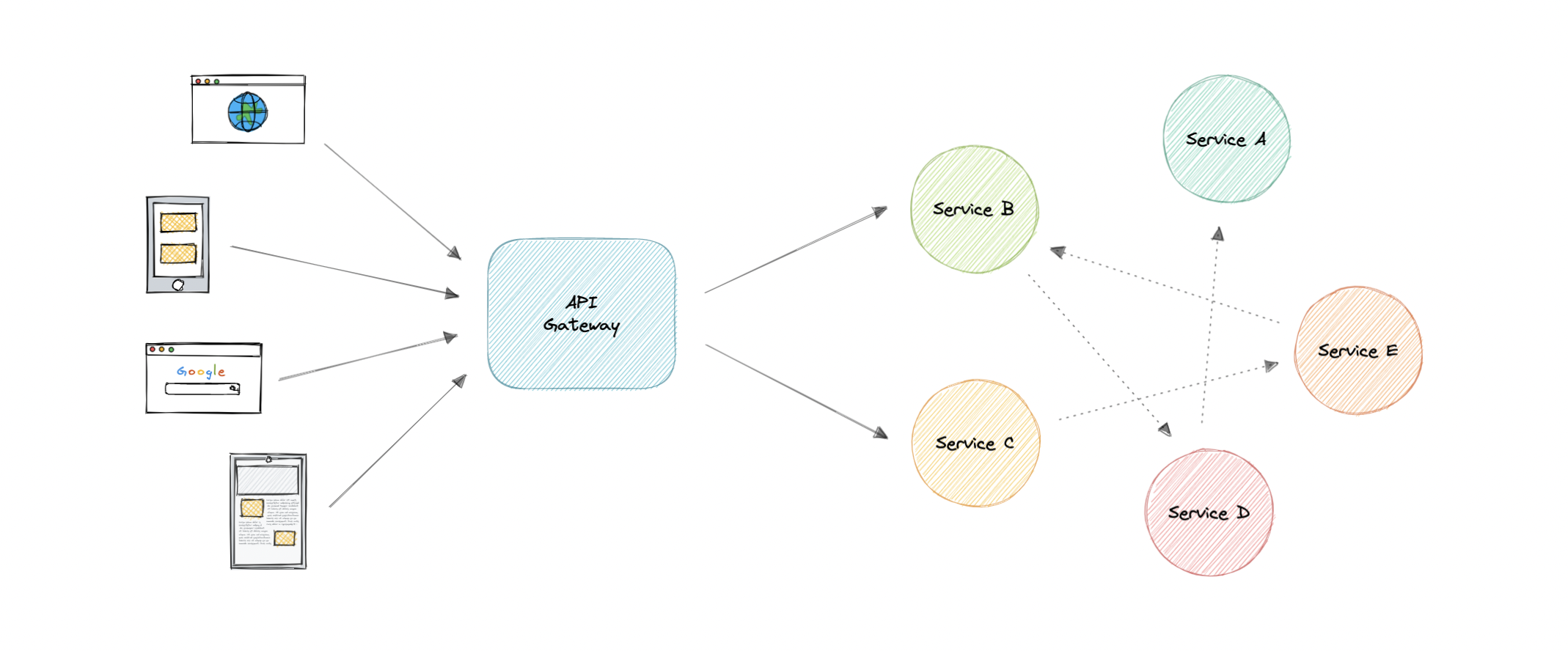
Why do we need an API Gateway?
The granularity of APIs provided by microservices is often different than what a client needs. Microservices typically provide fine-grained APIs, which means that clients need to interact with multiple services. Hence, an API gateway can provide a single entry point for all clients with some additional features and better management.
Features
Below are some desired features of an API Gateway:
- Authentication and Authorization
- Service discovery
- Reverse Proxy
- Caching
- Security
- Retry and Circuit breaking
- Load balancing
- Logging, Tracing
- API composition
- Rate limiting and throttling
- Versioning
- Routing
- IP whitelisting or blacklisting
Advantages
Let’s look at some advantages of using an API Gateway:
- Encapsulates the internal structure of an API.
- Provides a centralized view of the API.
- Simplifies the client code.
- Monitoring, analytics, tracing, and other such features.
Disadvantages
Here are some possible disadvantages of an API Gateway:
- Possible single point of failure.
- Might impact performance.
- Can become a bottleneck if not scaled properly.
- Configuration can be challenging.
Backend For Frontend (BFF) pattern
In the Backend For Frontend (BFF) pattern, we create separate backend services to be consumed by specific frontend applications or interfaces. This pattern is useful when we want to avoid customizing a single backend for multiple interfaces. This pattern was first described by Sam Newman.
Also, sometimes the output of data returned by the microservices to the front end is not in the exact format or filtered as needed by the front end. To solve this issue, the frontend should have some logic to reformat the data, and therefore, we can use BFF to shift some of this logic to the intermediate layer.
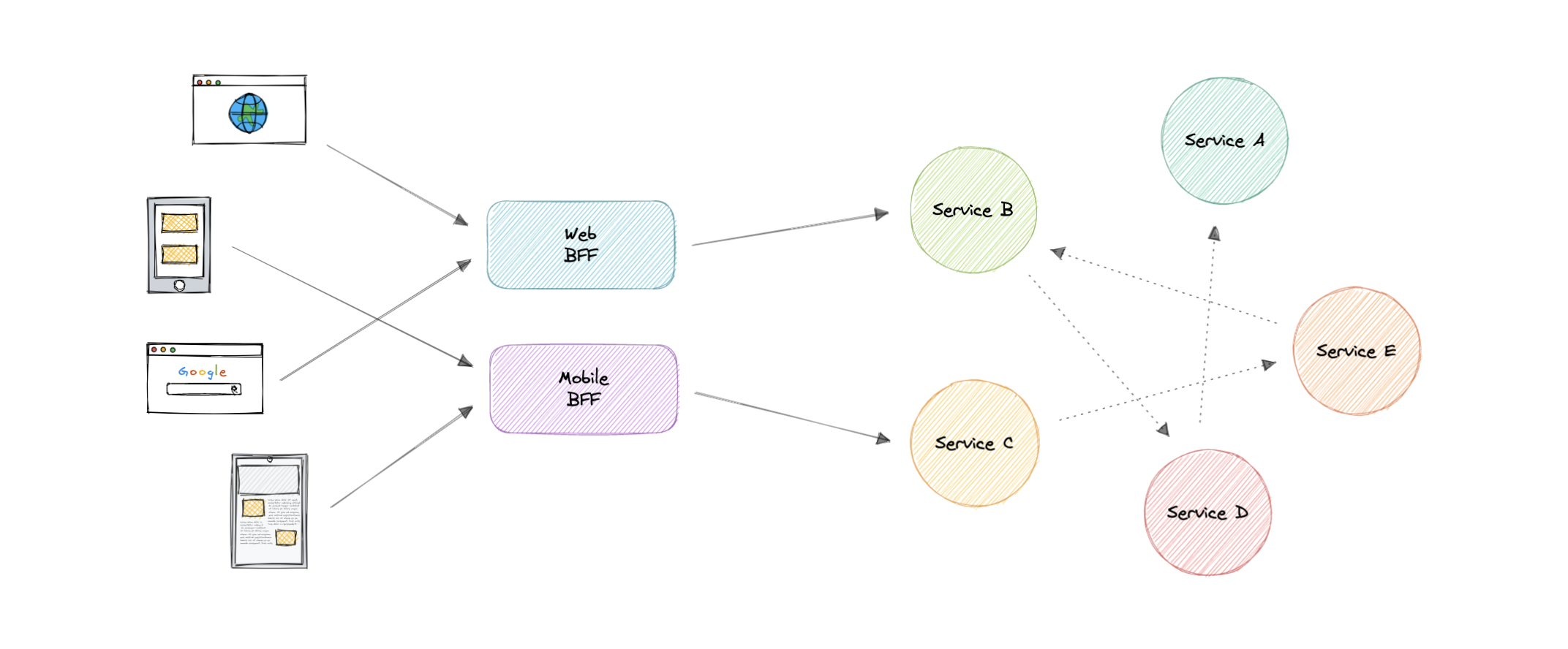
The primary function of the backend for the frontend pattern is to get the required data from the appropriate service, format the data, and sent it to the frontend.
GraphQL performs really well as a backend for frontend (BFF).
When to use this pattern?
We should consider using a Backend For Frontend (BFF) pattern when:
- A shared or general purpose backend service must be maintained with significant development overhead.
- We want to optimize the backend for the requirements of a specific client.
- Customizations are made to a general-purpose backend to accommodate multiple interfaces.
Examples
Following are some widely used gateways technologies: